News
Household Air Purifier: The Health Guardian of Indoor Air
Time:
2025-06-12
In modern life, people are paying increasing attention to indoor air quality. As a powerful assistant to improve indoor air quality, household air purifiers have gradually entered thousands of households. They can effectively remove indoor air pollutants, such as dust, pollen, odors, decoration pollutants like formaldehyde, bacteria, and allergens, significantly enhancing air cleanliness and safeguarding the health of family members.


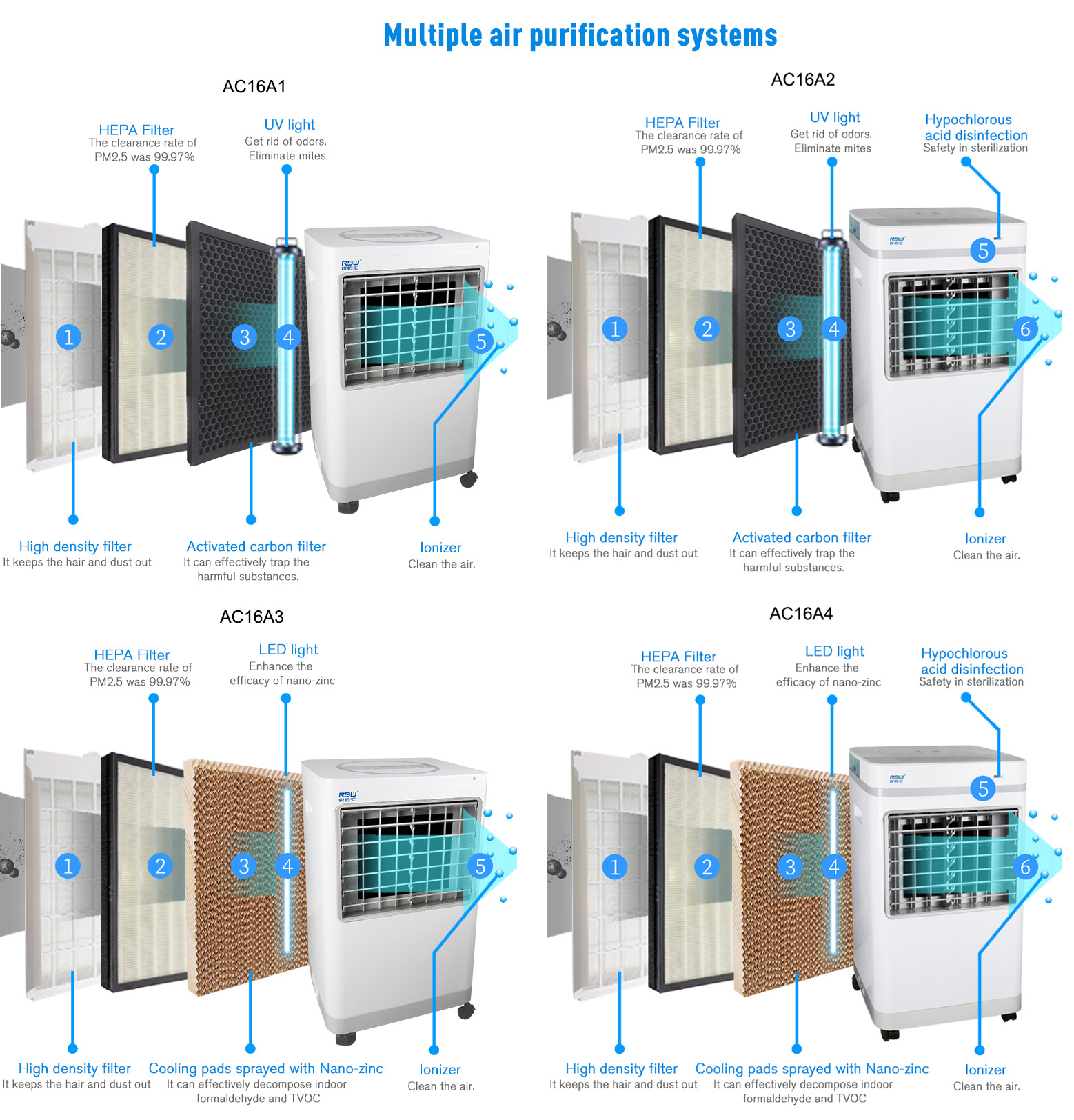
1. Working Principle
Household air purifiers typically consist of multiple systems working in coordination, including a high-voltage circuit, negative ion generator, ventilator, and air filter. When the purifier is in operation, the ventilator plays a key role in promoting the continuous circulation of indoor air. Polluted air is drawn into the machine and first passes through the layers of the air filter, where various pollutants are removed or adsorbed.Subsequently, the negative ion generator starts to work, continuously ionizing the air to produce a large number of negative ions. These negative ions are sent out by a micro-fan to form a negative ion flow, ultimately achieving the purpose of cleaning and purifying the air.
Common air particulate matter purification methods include:
Mechanical Filtration: Captures particles through three mechanisms: direct interception, inertial collision, and Brownian diffusion. It performs well in collecting fine particles but has the problem of high wind resistance. To ensure high purification efficiency, the filter element needs to have a dense structure and requires regular replacement.
Adsorption: Utilizes the large surface area and porous structure of materials to capture particulate pollutants. However, this method is prone to material blockage and is relatively more effective in removing gaseous pollutants.
Electrostatic Precipitation: Ionizes the gas through a high-voltage electrostatic field, making dust particles charged and adsorbed onto the electrodes. This method has low wind resistance but poor capture effect on larger particles and fibers, may cause discharge phenomena, and is troublesome and time-consuming to clean, easily producing ozone and causing secondary pollution.
Negative Ion and Plasma Methods: Charge air particles to make them coalesce into larger particles and eventually settle. However, it should be noted that particles are not truly removed from the air but only attached to nearby surfaces, which easily leads to re-dusting problems.
Electrostatic electret filtration: Taking 3M's "high-efficiency electrostatic air filter" as an example, it adopts breakthrough filter materials with permanent static electricity, which can effectively block particulate pollutants larger than 0.1 microns in the air, such as dust, dander, pollen, bacteria, etc. At the same time, its ultra-low impedance characteristics ensure the stable operation of air conditioners and maintain good cooling effects.
2. Main Technologies
Activated Carbon Adsorption Technology: Activated carbon has a rich porous structure, which enables it to efficiently adsorb odors and harmful gases in the air, such as formaldehyde and benzene. However, after activated carbon is saturated with adsorption, if it is not replaced in time, it may release the adsorbed pollutants back into the air, causing secondary pollution.
Ion Filtration Technology: Including negative ion and positive ion technologies. The principle is to charge air particles so that they are more easily adsorbed or settled. At the same time, ion filtration technology can also play a role in sterilization to a certain extent.
Ozone Sterilization Technology: Ozone has strong oxidizing properties and can effectively kill bacteria, viruses, and other microorganisms in the air. But ozone itself is a harmful gas, and excessive use may cause harm to human health. Therefore, when using ozone sterilization technology, the ozone release amount must be strictly controlled.
High-Efficiency Particulate Air Filter (HEPA): HEPA has a filtration efficiency of over 99.97% for 0.3-micron particles, which can extremely effectively filter fine particles in the air such as dust, pollen, and smoke. At present, it is one of the most widely used filtration technologies in air purifiers.
Electrostatic Precipitation Technology: Uses a high-voltage electrostatic field to ionize the gas, and the charged dust particles are adsorbed onto the electrodes. The advantage of this technology is low wind resistance, but it has poor capture effect on larger particles and fibers, is troublesome to clean, and is prone to produce ozone.
Photocatalyst Technology: Under the irradiation of ultraviolet light, photocatalyst materials can generate active substances such as hydroxyl radicals. These active substances can decompose organic pollutants in the air into carbon dioxide and water, thereby achieving multiple functions such as sterilization, deodorization, and decomposition of harmful gases.
3. Performance Indicators
Clean Air Delivery Rate (CADR): Reflects the purifier's ability to remove particulate matter or gaseous pollutants, including formaldehyde CADR and particulate matter CADR. Under the same conditions, the higher the CADR value, the higher the purification efficiency.
Cumulative Clean Mass (CCM): The larger the value, the larger the total amount of air that can be purified, and the longer the service life of the filter.
Purification Energy Efficiency: Measures the relationship between the electric energy consumed by the air purifier per unit time and the amount of purified air. The higher the energy efficiency ratio, the more energy-efficient the air purifier is.
Noise: Generally, 30-60dB is more appropriate. The lowest gear at 30dB is almost silent, and excessive noise may affect people's life and rest.
4. Usage Notes
Regularly Replace the Filter: The filter should be replaced every 6 months to 1 year.
Choose a Suitable Use Place: The air purifier should be placed in a well-ventilated place without obstacles to ensure smooth air circulation and achieve the best purification effect. Usually, larger spaces such as bedrooms and living rooms are more suitable use places. When placing it, avoid placing it against walls or furniture. It is best to place it in the middle of the room or keep a distance of more than 1m from the wall.
Pay Attention to the Switching Timing: In periods with poor air quality, such as during smog or after decoration, the air purifier should be turned on in time; when the indoor personnel are dense, it should also be turned on in a timely manner to ensure air quality. When people leave the room, the air purifier can be turned off, which can not only avoid unnecessary power waste but also extend the service life of the machine.
Control Humidity: Some air purifiers are equipped with a humidification function, but if the environmental humidity is too high, it may affect the effect of the filter. Therefore, maintaining a suitable indoor humidity (usually between 40% and 60%) is crucial. Too high or too low humidity will reduce the working efficiency of the air purifier.
Regularly Clean the Body: During the use of the air purifier, dust and dirt will accumulate on the body and the air inlet. Regular cleaning can improve the working efficiency of the air purifier and ensure the normal operation of the equipment. It should be noted that do not directly wash the filter with water to avoid damaging the filter and affecting the purification effect.
In short, choosing a household air purifier suitable for one's family and using and maintaining it correctly can create a fresh and healthy indoor air environment for family members. It is hoped that through the introduction of this article, everyone can find the most suitable one among the many air purifier products.
Our air purifier product have four models available for selection. For specific product information, please feel free to contact us.
Related News
Share to
Are you ready?
Start your project now!







